ALFASIGMA SpA
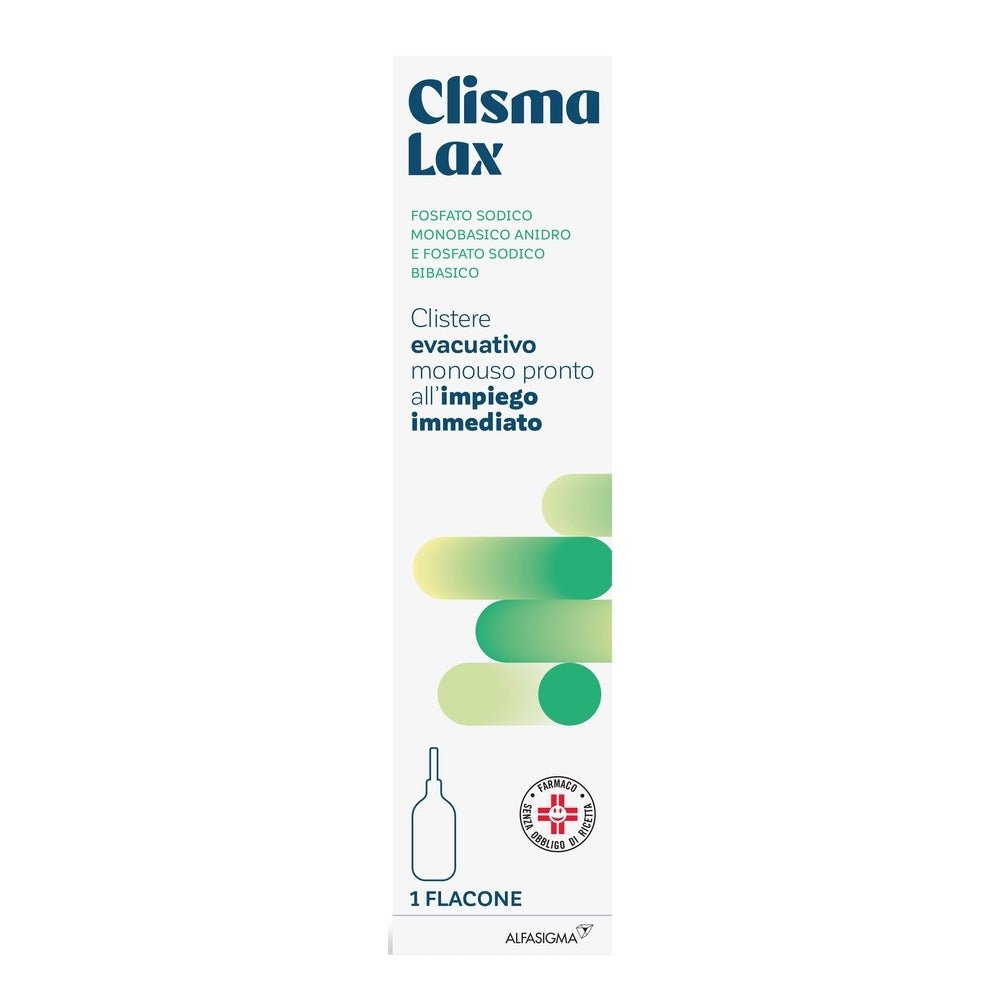
Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml
Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml

Pickup available at Farmacia Tili
Usually ready in 24 hours
PRODUCT NET WEIGHT
PRODUCT NET WEIGHT
EAN
EAN
024995033
MINSAN
MINSAN
024995033
Clisma Lax is a rectal solution indicated for the treatment of occasional constipation and for bowel preparation before diagnostic tests or surgical procedures . Thanks to its formulation with sodium phosphate , it acts quickly, promoting evacuation within a few minutes of application. The practical disposable bottle with pre-lubricated cannula ensures easy, safe and comfortable application. Ideal for those who need effective action without irritating the intestine.
ACTIVE INGREDIENTS
Active ingredients contained in Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml - What is the active ingredient in Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml?
100 ml contain 13.91 g of sodium phosphate monobasic anhydrous (NaH 2 PO 4 ); 3.18 g of sodium phosphate dibasic (Na 2 HPO 4 ). Excipients with known effect: sodium benzoate (100 mg per 100 ml) and methyl parahydroxybenzoate (50 mg per 100 ml). For the full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
EXCIPIENTS
Composition of Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml - What does Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml contain?
Sodium hydroxide, sodium benzoate, methyl parahydroxybenzoate, purified water.
DIRECTIONS
Therapeutic indications Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml - Why is Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml used? What is it for?
Short-term treatment of occasional constipation.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS
Contraindications Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml - When should Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml not be used?
-Hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1. - acute or unknown abdominal pain - nausea or vomiting - intestinal obstruction or stenosis or anorectal stenosis - intestinal sub-occlusion - mechanical ileus - paralytic ileus - inflammatory intestinal disorders and other conditions that may increase the absorption of the medicinal product - anal perforation - congenital or acquired megacolon - Hirschsprung's disease - rectal bleeding of unknown origin - acute haemorrhoidal crisis with pain and bleeding - severe dehydration - children under twelve years of age. Phosphates are contraindicated in patients with cardiac disorders, severe renal insufficiency or in the presence of hyperphosphatemia. Other preparations containing sodium phosphates, including oral solutions or tablets of sodium phosphates, should not be administered simultaneously (see section 4.5).
DOSAGE
Quantity and method of taking Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml - How to take Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml?
Dosage Adults and adolescents (12-18 years): the entire dose of the bottle. Method of administration Do not exceed the recommended doses. Laxatives should be used as infrequently as possible and for no more than seven days. Use for longer periods of time requires a doctor's prescription after adequate evaluation of the individual case. Take preferably in the evening.
CONSERVATION
Storage Enema Lax rectal solution 133ml - How do you store Enema Lax rectal solution 133ml?
This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions.
WARNINGS
Warnings Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml - About Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml it is important to know that:
Paediatric population : The 133 ml bottle should not be used in children under 12 years of age. Laxative abuse (frequent or prolonged use or excessive doses) may cause persistent diarrhoea with consequent loss of water, mineral salts (especially potassium) and other essential nutrients. In more severe cases, dehydration or hypokalaemia may occur, which may lead to cardiac or neuromuscular dysfunction, especially in case of concomitant treatment with cardiac glycosides, diuretics or corticosteroids. Patients should be encouraged to drink fluids to help prevent dehydration, particularly patients with conditions that may predispose to dehydration, or those taking medicinal products that may decrease the glomerular filtration rate, such as diuretics, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors), angiotensin receptor blockers (sartans) or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Since Clisma lax contains sodium phosphates, there is a risk of high serum sodium and phosphate levels and decreased calcium and potassium levels, and consequently hypernatremia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia and hypokalemia, which may occur with clinical signs such as tetany and renal failure. Laxative abuse may cause dependence (and, therefore, possible need to gradually increase the dosage), chronic constipation and loss of normal intestinal functions (intestinal atony). Repeated use of laxatives may give rise to habituation or damage of various types. Prolonged use of a laxative for the treatment of constipation is not recommended. Pharmacological treatment of constipation should be considered an adjuvant to hygienic-dietetic treatment (e.g. increased vegetable fibre and liquids in the diet, physical activity and re-education of intestinal motility). The treatment of chronic or recurrent constipation always requires the intervention of a doctor for diagnosis, prescription of drugs and monitoring during therapy. A careful evaluation by a doctor is essential when the need for a laxative arises from a sudden change in previous bowel habits (frequency and characteristics of bowel movements) that lasts more than two weeks or when the use of a laxative fails to produce effects. It is advisable that elderly or unhealthy subjects and patients with uncontrolled arterial hypertension, ascites, heart disease, changes in the rectal mucosa (ulcers, fissures), consult their doctor before using the medicine. Patients should be advised to stop administration if resistance is encountered, since the forced administration of the enema can cause lesions. In episodes of constipation, it is recommended first of all to correct eating habits by integrating the daily diet with an adequate intake of fiber and water. When using laxatives, it is advisable to drink at least 6-8 glasses of water or other liquids a day to help soften the stool.
INTERACTIONS
Interactions Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml - Which medicines or foods can modify the effect of Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml?
Systemic absorption of sodium phosphate rectal solution is limited, however in some conditions it may be increased and predispose to possible interactions with other drugs. Concomitant use of drugs that can affect electrolyte balance (such as diuretics, corticosteroids, calcium antagonists, lithium) may facilitate the onset of hyperphosphatemia, hypercalcemia and hypernatremia. Patients taking drugs that can prolong the QT interval may be at greater risk of developing this adverse reaction if treated concomitantly with sodium phosphate. Since hypernatremia is associated with low lithium levels, concomitant use of Clisma lax and lithium may cause a reduction in serum lithium levels, with a decrease in efficacy. Concomitant use of calcium supplements or calcium-containing antacids may increase the risk of ectopic calcification. Other preparations containing sodium phosphates, including oral solutions or sodium phosphate tablets, should not be administered concomitantly (see section 4.3).
SIDE EFFECTS
Like all medicines, Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml can cause side effects - What are the side effects of Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml?
The following are the adverse reactions of sodium phosphate organised according to the MedDRA system organ classification. There are insufficient data to establish the frequency of the individual effects listed. Immune system disorders Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. urticaria) Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Blisters, itching, burning Gastrointestinal disorders Isolated cramp-like pain or abdominal colic and diarrhoea, with loss of fluids and electrolytes, more frequent in cases of severe constipation, as well as irritation at the rectal level. Nausea, vomiting. Metabolism and nutrition disorders Hyperphosphatemia, hypokalaemia, hypernatraemia, hypocalcemia and tissue calcification may rarely occur. Reporting of suspected adverse reactions Reporting suspected adverse reactions that occur after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via the national reporting system at www.aifa.gov.it/content/segnalazioni-reazioni-avverse.
OVERDOSE
Overdose Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml - What are the risks of Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml in case of overdose?
The most frequently observed effect following ingestion or rectal administration is gastrointestinal irritation (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea). Persistent diarrhoea results in loss of water, mineral salts (especially potassium) and other essential nutrients. Fluid and electrolyte losses must be replaced. Electrolyte imbalances are characterised by the following symptoms: thirst, vomiting, weakness, oedema, bone pain (osteomalacia) and hypoalbuminaemia. In more severe cases, dehydration or hypokalaemia may occur, which may lead to cardiac or neuromuscular dysfunction, especially in the case of concomitant treatment with cardiac glycosides, diuretics or corticosteroids. Fluid and electrolyte losses must be replaced. Conservative measures are generally sufficient; plenty of fluids should be administered, especially fruit juices. See also section 4.4 regarding laxative abuse. If a significant amount of phosphate is absorbed, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia may occur. Alterations in fluid and electrolyte balance have been observed following oral, rectal, and intravenous exposure. Severe hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia may cause tetany, convulsions, bradycardia, QT prolongation, arrhythmia, coma, and cardiac arrest. Severe dehydration, hypernatremia, hypotension, metabolic acidosis, and tachycardia may also occur. The elderly, children, and patients with renal insufficiency are at increased risk of toxic effects.
PREGNANCY AND BREASTFEEDING
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies on the use of the medicinal product during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Therefore, the medicinal product should be used only when necessary, under the direct supervision of a doctor, after evaluating the expected benefit for the mother in relation to the possible risk for the fetus or the infant.
DRIVING AND USE OF MACHINERY
Taking Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml before driving or using machinery - Does Clisma Lax rectal solution 133ml affect driving or using machinery?
The medicine does not alter the ability to drive vehicles or use machinery. However, it is possible that during treatment some side effects may occur, therefore it is good to know the reaction to the medicine before driving vehicles or using machinery.